1. Name of entrepreneur/ Name of entrepreneur's business/complete address (including zipcode)
-Mr. Anderson, Dance 411, 475 Moreland Ave. Atlanta Ga. 30316
2. Type of business organization
-A dance company
3. Length of time the business has been in operation
-Nine years
4. List products provided by the business (goods and services)
-Offer Dance
-Teen Building
-Weight Loss Program
- Core and Strength Training
5. Number of employees/skills needed to work in the business
-There are twenty three employees and you will need at least a high school diploma and some positions require college degrees.
6. List benefits of business to community/What does this business provide that similar businesses don't provide
-This business provides outreach services
-Frequently have donation funds
-Provide jobs for the local communities
- A safe haven for local children
-Well rounded programs for all age groups
7. Major competitor for this business and how this business remains competitive
-Major competitor: small dance studios, and individual dance instuctors.
-Remains competitive by offering classes that are fun, energetic, and have reasonable prices.
8. Descibe methods used to increase growth of business and any future plans for expansion
- Strong marketing tactics
-Radio covers
-Annual dance benefits recitals
9. Three greatest challenges in operating the business
-Balancing your books (making sure at the end of the month your not losing money.)
-Making sure that you have continued to provide excellent customer service
-Keeping class prices reasonable
10. Three greatest rewards in operating the business
-Seeing someone achieve their weight loss goals
-Someone at the begginning of the class say they couldn't dance and at the end being able to finish the class with confidence
-Being self employeed
Compare and Contrast Monopoly and Oligopoly; Monopolistic Competition. Must include at least 2 characteristics for each. Provide two examples for each type of company.
-Monopoly: The single seller makes a product that has no good substitute. Other firms may be able to produce the good or service but choose not to enter the market or are barred from it. Characteritics: One unique; no close substitutes considerable. Ex. local utilities, post office! government runs monopoly.
-Oligopoly: A few sellers make products that are good, but not perfect substitutes. Consumers can be included to change suppliers but have only a limited number of choices. A few firms dominate large shares of the market and set prices Ex. pepsi, coca cola, proctor and gamble, johnson and johnson, etc. Characteritics: few standardized or differentiated
- Monopolistic Competition: The market has many firms but each supplier's product is differentiated. Consumers can be included to change brands but they have brand preferences. Characteristics: Many differentiated. Ex. Retail trade, dresses, shoes, etc.
Tuesday, October 5, 2010
Economic Goals; Role of Government; Economic Growth and Productivity
1. How are the economic goals of freedom, security, efficiency, equity, stability, and economic growth achieved in a market economy?
In a market, economic freedom is the freedom to work (or not), freedom to produce, trade and consume any goods and services acquired without the force, fraud or theft.
In a market, economic security is the condition of having stable income or other resources to support a standard of living now and in the foreseeable future. It includes probable continued solvency (assests exceed liabilities), predictability of the future cash flow of a person or other economic entity, such as a country, and employment security or job security.
In a market, economic efficiency is said to be more efficient than another if it can provide more goods and services for society without using more resources.
In a market, economic equtity refers to what is fair. Generally, the apportionment (distribution) of resources or goods among the people is considered fair.
In a market, economic stability is the absence of excessive fluctuations in the economy. Ex. high unemployment.
In a market, economic growth is the process by which a nation's wealth increases over time. The most widely used measure of economic growth is GDP, the country's total output of goods and services.
2. Why has the role of government in the economy increased dramatically since the 1880s? The government had to maintain social and legal framework. Providing public goods and services, maintain competition, redistribute income, correcting for externalities, and stabilize the economy.
3. Write an arguement that supports or opposes the statement in the visual below that says "deregulation won't work because people are greedy"? Deregulation is the removal of some government controls over a market. If the government isn't in conrol the people will take advantage and have more freedom to do what they want to do which is a bad idea.
4. Explain why the government provides public goods and services? Why are these public goods and services NOT provided by the private sector? (please include a discussion on non-rivalrous and non-excludable goods) The government provides public good and services because they have to be non-rivalrous and non- excludable so that everyone can have access to these goods. If private sectors provided these goods, they would not be non-rivalrous and non-excludable.
5. What are the 6 functions of government in a market economy (provide an example of how the government fulfills each of these 6 functions)? 1. Maintaining Legal and Social Framework (Ex. Create laws and provide courts, provide info. and services to help economy function better, establish a monetary system, define and enforce property rights.) 2. Providing Public Goods and Services (Ex. Provide goods and services that markets are unable or unwilling to provide, such as national defense.) 3. Maintaining Competition and Protecting Profits (Ex. Create and enforce antitrust laws; regulate natural monopolies.) 4. Redistributing Income (Ex. Higher income tax rates for rich than for poor, provide social security, and aid to dependent children, medicare, medicaid.) 5. Correcting for Externalities (Ex. Taxes to reduce negative externalities, such as education. Externalaties exist when some of the costs or benefits associated with the production or consumption of a product "spill over" to third parties other than the direct producer or consumer of the product.) 6. Stabilizing the Economy (Ex. Use government budgets and/or the money supply to promote economic growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment.)
6. Describe the relationship that inputs and outputs have on productivity? The input is hard work a worker put in to get a good outcome which is the output. The work that is done will improve the business output.
7. How do investments in capital goods, technology, human capital, training, and educating workers, improve productivity and economic growth? You invest into capital goods, technology, human capital, training, and educating workers that improves productivity because smarter workers find ways to complete more work in less time. Human capital and technology increases productivity because they aid the workers so that more work can be completed.
8. Refer to the chart below and explain the cause of the decrease in the output, productivity, and employment in manufacturing in the United States. What can the United States do to reverse this downward trend in manufacturing? Deregulations has more ups than downs. In this chart, because people are being greedy. The effect of not having the government involved is exemplified.
In a market, economic freedom is the freedom to work (or not), freedom to produce, trade and consume any goods and services acquired without the force, fraud or theft.
In a market, economic security is the condition of having stable income or other resources to support a standard of living now and in the foreseeable future. It includes probable continued solvency (assests exceed liabilities), predictability of the future cash flow of a person or other economic entity, such as a country, and employment security or job security.
In a market, economic efficiency is said to be more efficient than another if it can provide more goods and services for society without using more resources.
In a market, economic equtity refers to what is fair. Generally, the apportionment (distribution) of resources or goods among the people is considered fair.
In a market, economic stability is the absence of excessive fluctuations in the economy. Ex. high unemployment.
In a market, economic growth is the process by which a nation's wealth increases over time. The most widely used measure of economic growth is GDP, the country's total output of goods and services.
2. Why has the role of government in the economy increased dramatically since the 1880s? The government had to maintain social and legal framework. Providing public goods and services, maintain competition, redistribute income, correcting for externalities, and stabilize the economy.
3. Write an arguement that supports or opposes the statement in the visual below that says "deregulation won't work because people are greedy"? Deregulation is the removal of some government controls over a market. If the government isn't in conrol the people will take advantage and have more freedom to do what they want to do which is a bad idea.
4. Explain why the government provides public goods and services? Why are these public goods and services NOT provided by the private sector? (please include a discussion on non-rivalrous and non-excludable goods) The government provides public good and services because they have to be non-rivalrous and non- excludable so that everyone can have access to these goods. If private sectors provided these goods, they would not be non-rivalrous and non-excludable.
5. What are the 6 functions of government in a market economy (provide an example of how the government fulfills each of these 6 functions)? 1. Maintaining Legal and Social Framework (Ex. Create laws and provide courts, provide info. and services to help economy function better, establish a monetary system, define and enforce property rights.) 2. Providing Public Goods and Services (Ex. Provide goods and services that markets are unable or unwilling to provide, such as national defense.) 3. Maintaining Competition and Protecting Profits (Ex. Create and enforce antitrust laws; regulate natural monopolies.) 4. Redistributing Income (Ex. Higher income tax rates for rich than for poor, provide social security, and aid to dependent children, medicare, medicaid.) 5. Correcting for Externalities (Ex. Taxes to reduce negative externalities, such as education. Externalaties exist when some of the costs or benefits associated with the production or consumption of a product "spill over" to third parties other than the direct producer or consumer of the product.) 6. Stabilizing the Economy (Ex. Use government budgets and/or the money supply to promote economic growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment.)
6. Describe the relationship that inputs and outputs have on productivity? The input is hard work a worker put in to get a good outcome which is the output. The work that is done will improve the business output.
7. How do investments in capital goods, technology, human capital, training, and educating workers, improve productivity and economic growth? You invest into capital goods, technology, human capital, training, and educating workers that improves productivity because smarter workers find ways to complete more work in less time. Human capital and technology increases productivity because they aid the workers so that more work can be completed.
8. Refer to the chart below and explain the cause of the decrease in the output, productivity, and employment in manufacturing in the United States. What can the United States do to reverse this downward trend in manufacturing? Deregulations has more ups than downs. In this chart, because people are being greedy. The effect of not having the government involved is exemplified.
Reflection: What are two questions that you still have about these particular standards? What way would market economy be useful? How do inputs and outputs show scarcity?
1. Why was this assignment so confusing?
2. Does Deregulation have anything to do with the government?
Market economy is useful because economic decisions and the pricing of goods and services are guided solely by the aggregate interactions of a country's citizens and businesses and there is little government intervention or central planning.
Inputs and Outputs show scarcity because if the input isn't good enough in a business the output will be bad causing the business to loose money which will cause scarcity. The business will go bad!
Monday, September 27, 2010
Microeconomics-Standards Based Blog M11 and M12
Microeconomics
1. Using the typical 'Facebook' lingo, write a definition for Microeconomics and then provide a standard English translation for your 'Facebook' definition. -Microeconomics: This means operations being studied of a national economy. (facebook lingo)
-Microeconomics: The study of the operations of the components of a national economy, such as individual firms, households, and consumers. (standard english translation)
Role of Money- M11

-Real Money is a medium that can be exchanged for goods and services and is used as a measure of their values on the market, including among its forms a commodity such as gold, an officially issued coin or note, or a deposit in a checking account or other readily liquefiable account.
-Play Money has no value in our society.
2. Money has no actual value other than the value we attach to it. The barter system would still be practiced today if the participants did not agree to set a value on a piece of printed paper that represented the value of the goods and services they had to offer. What would you accept in place of money, if someone wanted to 'buy' your most prized material possession?
-I would accept gold because you can keep it for store of value.
Circular Flow Model- M11

1. What does a circular flow model tell us?
-The circular flow of income is a simple model of the economy showing flows of goods and services and factors of production between firms and households in a market economy. It is a graphic representation
of the relationships of the Business (producer) Sector and Household (consumer) Sector and the product (goods and services) and Resource Markets (factors of production) in a market economy. Government also purchases goods and services from businesses and the factor of productions from household.
2. What is the role of households in the three sector circular flow model?
-Households (consumers) provide businesses with payments in exchange for jobs and goods and services. Households also pay taxes to the government, helping the government receive needed revenue.
3.What is the role of businesses in the three sector circular flow model?
-Businesses provide goods, and services to households, for the government businesses pay taxes, and supply goods and services.
4.What is the role of government in the three sector circular flow model?
-The government supply services and income to households, and gives services and payments to businesses.
-The government supply services and income to households, and gives services and payments to businesses.
5. What role do households have in the factors or resource market (inputs)? Households own land, labor, capital goods, and entrepreneurship.
Law of Demand and Law of Supply- M12
1. For each event described below, explain what happens to either the demand or supply curve. (increase/decrease? Shifts left or right?)
b). What happens to the supply of orange juice if Florida is hit with very severe weather? The quanity supplied will decrease and the price will increase because the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied.
c). In the market for coffee, severe global weather systems destroy 30% of the coffee bean crop.
Unfortunately the supply will decrease, because the coffee bean crop is destroyed.
d). In the market for cereal, if the price of cardboard material used to package cereal increases.
The supply will decrease unless the consumers really love cereal and will pay the new price.
2. For each part below, EXPLAIN what happens to equilibrium quantity and price(increase or decrease?).
a). In the market for doughnuts, if they were found to be a major contributor to high cholesterol in adults.
The demand will go down and there will be a surplus of doughnuts in businesses which will drive down the prices of doughnuts.
b). In the market for doughnuts, if widespread unemplyoment continues.
There will be a shift in supply to the left because less doughnuts will be produced and the price will drop on them.
c). In the market for doughnuts, if Krispy Kreme introduces a new whole wheat 'low-calorie' doughnut.
The demand will rise because it's healthy and alot of people will want to purchase it.
3. What are two factors that can change the quanity demanded? Provide an example for each.
-The buyers: income can change
- Consumer: preferences can change
4. What are two factors that can change the quantity supplied. Provide an example for each.
-Number of buyers goes up or down, or more suppliers enter the market. Ex. If the product has good quality more ppl will purchase it but if not then less people would purchase it. People like to get their money's worth.
Reflection: What are two questions that you have about standards M11 and M12.
1. How do the changes of demand affect the price?
2. What are the injections into a circular flow of income?
Tuesday, August 31, 2010
How Different Economic Systems Answer the Three Basic Economic Questions
1. The three basic economic questions that every society must answer is: Wh
at will be produced, How it will be produced, and For Whom will it be produced!
2. An economic system is the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of
an economy. The four types of economic systems are: Market, Command, Traditional, and Mixed. An example of market is the United States, and Germany. An example of command is china. An example of traditional is native americans tribe. An example of mixed is also the United States and other countries.
3. Market involves the U.S buyers and sellers. Command is planned and directed by government, where resources are allocated to factors by the state through created planning. Traditional is based on customs and beliefs. Mixed is where the government is involved and other buyers and sellers.
4. The United States reflect a combination of economic systems because the government is very involved in the U.S economy.
5. Traditional is used by the Inuit because they are a tribe and traditional is based on customs and beliefs.
6. I support Adam Smith theory because I don't feel as if the governor should be involved with consumers and sellers that should be left up with their beliefs and ideas. I oppose because the governor should be there to regulate what's going on and keeping everything in order.
at will be produced, How it will be produced, and For Whom will it be produced!
2. An economic system is the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of
an economy. The four types of economic systems are: Market, Command, Traditional, and Mixed. An example of market is the United States, and Germany. An example of command is china. An example of traditional is native americans tribe. An example of mixed is also the United States and other countries.
3. Market involves the U.S buyers and sellers. Command is planned and directed by government, where resources are allocated to factors by the state through created planning. Traditional is based on customs and beliefs. Mixed is where the government is involved and other buyers and sellers.
4. The United States reflect a combination of economic systems because the government is very involved in the U.S economy.
5. Traditional is used by the Inuit because they are a tribe and traditional is based on customs and beliefs.
6. I support Adam Smith theory because I don't feel as if the governor should be involved with consumers and sellers that should be left up with their beliefs and ideas. I oppose because the governor should be there to regulate what's going on and keeping everything in order.
Thursday, August 26, 2010
Production Possibilities Curve; Rational Decision Making; and Specialization
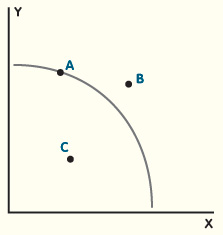
1. If you owned a business, what would a production possibilities curve tell you? Be specific. What are two factors that could cause your production possibilities curve to shift outward?
-The possibilities curve is a graphical representation of the alternative combinations of goods and services an economy can produce. It illustrates the production possibilities model. It shows you how much of two products you can produce with your resources. Two factors that would cause your production possibilities curve to shift outward is when there is an improvement in technology that would benefit both types of goods. An increase in the workforce which would result in mor factor resources being exploited. An improvment in productivity and effeciency in goods production.
2. What is the best way to determine whether or not we are making a rational economic decision?
-If your marginal benefit equal or exceed the marginal cost. Ex. If you buy a shirt it should have good quality, and it should be worth the amount of money you spent on it.
3. Why do companies choose to specialize and trade? What would happen if companies did not choose to specialize?
-Companies choose to specialize and trade because there is more money in trade. It also helps them save. (more bang for your buck)
-If companies choose not to specialize then the company will not do as good as their competitors. It is also a possibility that they may go bankrupt.
4. Include to relevant visuals (based on standards)
5. How do you feel about your knowledge of this standard? What are two questions that you have about this standard?
-I feel as if the standard becomes easy after you begin to study it enough. Everyday I learn something new.
- When there is excessive unemployment, What is the effect on production possibilities curve? Why does a production possibilities curve have a bowed out shape?
-The possibilities curve is a graphical representation of the alternative combinations of goods and services an economy can produce. It illustrates the production possibilities model. It shows you how much of two products you can produce with your resources. Two factors that would cause your production possibilities curve to shift outward is when there is an improvement in technology that would benefit both types of goods. An increase in the workforce which would result in mor factor resources being exploited. An improvment in productivity and effeciency in goods production.
2. What is the best way to determine whether or not we are making a rational economic decision?
-If your marginal benefit equal or exceed the marginal cost. Ex. If you buy a shirt it should have good quality, and it should be worth the amount of money you spent on it.
3. Why do companies choose to specialize and trade? What would happen if companies did not choose to specialize?
-Companies choose to specialize and trade because there is more money in trade. It also helps them save. (more bang for your buck)
-If companies choose not to specialize then the company will not do as good as their competitors. It is also a possibility that they may go bankrupt.
4. Include to relevant visuals (based on standards)
-I feel as if the standard becomes easy after you begin to study it enough. Everyday I learn something new.
- When there is excessive unemployment, What is the effect on production possibilities curve? Why does a production possibilities curve have a bowed out shape?
Tuesday, August 24, 2010
Limited Resources and Unlimited Wants- BreAnna Kennedy
1. How does scarcity influence the choices you make about how you spend your money? Give a specific example of a trade off that you had to make. What was the opportunity cost of your decision? How did you make your decision? Afterwards, how did you feel about youer choice?
-Your not going to spend more money that what you have coming in.
- Once when i was broke i pawned my mp3 player for money.
- I gained the money and had extra money in my pocket.
- First i was hesistant but i needed the money.
- I felt relieved because I had money in my pocket.
- The opportunity cost was losing the pleasure of listening to my mp3 player.
2. There are four factors of production- land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. How do business owners influence each of these factors of production? What is a risk and a reward that business owners might incur with each of the four factors of productions?
- Every decision there is to make dealing with the four factors of production the owner will have to make.
- The risk for land could be the owner not knowing anything about the area. The area could have all kinds of issues. The reward could be good because the business may be full with customers just by the area being good or in a busy community and if the business have customers then the owner makes money.
-The risk for labor could be the owner not hiring enough workers then the business will not run functional, just by the owner being cheap trying to save money. The business won't benefit you and may not be successful. The reward could be hiring enough workers to get the job done and having a well ran business so your happy and so are the customers.
-The risk for capital could be you not having enough supplies for your business. The reward may be you having more than enough supplies. That will be good for your business looks and needs.
-The risk for entrepreneurship could be frustration, stress, depression, exhaustion, etc. Entrepreneurs face alot trying to run a good business, wanting everything to go smoove and well is not easy. The reward for entrepreneurship is you controlling what goes on in your business. Ex. Your work hours, employees, decisions, etc.
3. Do you see yourself more as an individual that will supply labor or as an entrepreneur who make decisions about the use of labor? explain how you reached this conclusion.
-Your not going to spend more money that what you have coming in.
- Once when i was broke i pawned my mp3 player for money.
- I gained the money and had extra money in my pocket.
- First i was hesistant but i needed the money.
- I felt relieved because I had money in my pocket.
- The opportunity cost was losing the pleasure of listening to my mp3 player.
2. There are four factors of production- land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. How do business owners influence each of these factors of production? What is a risk and a reward that business owners might incur with each of the four factors of productions?
- Every decision there is to make dealing with the four factors of production the owner will have to make.
- The risk for land could be the owner not knowing anything about the area. The area could have all kinds of issues. The reward could be good because the business may be full with customers just by the area being good or in a busy community and if the business have customers then the owner makes money.
-The risk for labor could be the owner not hiring enough workers then the business will not run functional, just by the owner being cheap trying to save money. The business won't benefit you and may not be successful. The reward could be hiring enough workers to get the job done and having a well ran business so your happy and so are the customers.
-The risk for capital could be you not having enough supplies for your business. The reward may be you having more than enough supplies. That will be good for your business looks and needs.
-The risk for entrepreneurship could be frustration, stress, depression, exhaustion, etc. Entrepreneurs face alot trying to run a good business, wanting everything to go smoove and well is not easy. The reward for entrepreneurship is you controlling what goes on in your business. Ex. Your work hours, employees, decisions, etc.
3. Do you see yourself more as an individual that will supply labor or as an entrepreneur who make decisions about the use of labor? explain how you reached this conclusion.
- I see myself as an entrepreneur because someday i would love to be a psychiatrist, not only that but I would like to own the business. I've reached my conclusion because i am independent, determined, and want to be a boss of my own one day in life.
4. Include two relevant visuals (based on standards) with captions that explain their significance to the standard(s)
5. How do you feel about your knowledge of this standard? What are two questions that you have about this standard?
-I feel sort of smart because I've come a long way with these standards. First I was kind of lost but now I understand It well.
- How exspensive is it to own my own business? How do I become a successful entrepreneur?
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)